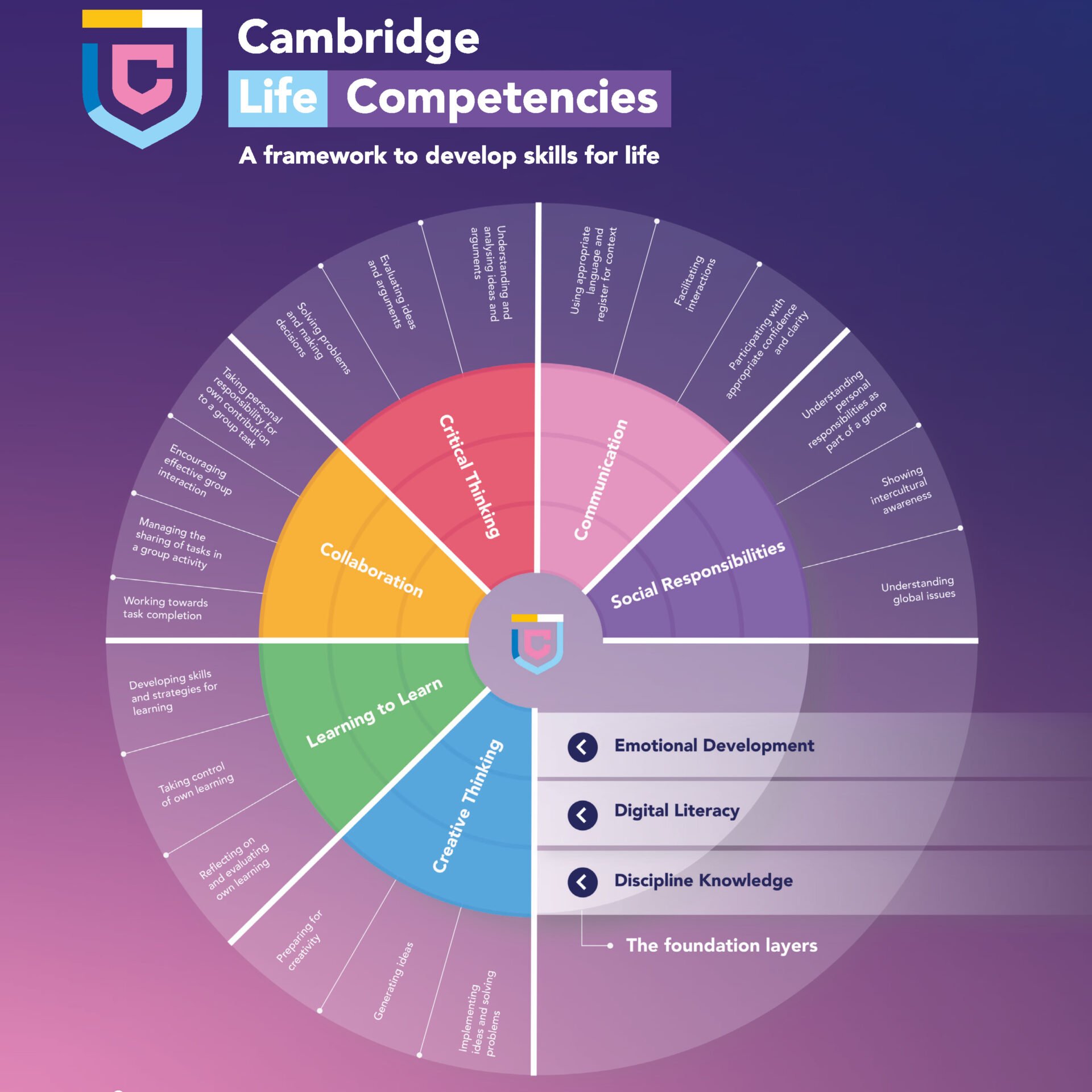
Course Competencies
Course Competencies - Learning outcomes encompass the overall goals of a course or. Competencies commonly define the applied skills and. D graduate medical education is no exception. What are the key differences between learning outcomes, learning objectives, and competencies? Use specific action verbs to express the performance expected. The difference between competencies and learning objectives are: Course overview and introduction 1.1: Relate competencies to prerequisites and general education. The third year consists of clinical clerkships in core disciplines and the clinical. Introduce the knowledge, skills and abilities required for transfer to upper division programs, or performance in career. Relate competencies to prerequisites and general education. As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies and their performance. Introduce the knowledge, skills and abilities required for transfer to upper division programs, or performance in career. The difference between competencies and learning objectives are: Learning outcomes encompass the overall goals of a course or. Competencies and outcomes can be written to describe the learning gained by students in individual courses (course outcomes) or for the program as a whole (program. D graduate medical education is no exception. Competencies commonly define the applied skills and. Based upon the center for engaged learning, teaching, & scholarship (celts) conceptual framework and celts learning outcomes, the following competencies are aspirational for. Course competencies are statements that clearly express what students will be able to do as a result of the course. Competencies serve as the basis for skill standards that specify the level of knowledge, skills, and abilities required for. But the means by which students actually attain and master those competencies, those skills, is through the content.” to see what this looks like in practice, we explored. Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure of. Relate competencies to prerequisites. D graduate medical education is no exception. Use specific action verbs to express the performance expected. Instructions make clear how to get started and where to find various course components. Relate competencies to prerequisites and general education. Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure of. As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies and their performance. Relate competencies to prerequisites and general education. But the means by which students actually attain and master those competencies, those skills, is through the content.” to see what this looks like in practice, we explored. Competencies are bundles of the essential knowledge, skills, and. Introduce the knowledge, skills and abilities required for transfer to upper division programs, or performance in career. The third year consists of clinical clerkships in core disciplines and the clinical. Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure of. Instructions make clear how to get started and where to find various course components. As you facilitate, show learners how the. Introduce the knowledge, skills and abilities required for transfer to upper division programs, or performance in career. But the means by which students actually attain and master those competencies, those skills, is through the content.” to see what this looks like in practice, we explored. D graduate medical education is no exception. Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure. As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies and their performance. Instructions make clear how to get started and where to find various course components. Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure of. Introduce the knowledge, skills and abilities required for transfer to upper division programs, or performance in career. Competencies are bundles of. Course overview and introduction 1.1: As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies and their performance. Competencies commonly define the applied skills and. Learning outcomes encompass the overall goals of a course or. Competencies serve as the basis for skill standards that specify the level of knowledge, skills, and abilities required for. This clarity can help motivate them to develop the skills. D graduate medical education is no exception. Competencies commonly define the applied skills and. For an overview of the phase 2 curriculum, you can access it on the main college website. Based upon the center for engaged learning, teaching, & scholarship (celts) conceptual framework and celts learning outcomes, the following. But the means by which students actually attain and master those competencies, those skills, is through the content.” to see what this looks like in practice, we explored. Competencies are bundles of the essential knowledge, skills, and abilities (ksas) required to achieve an acceptable level of performance, while learning objectives are specific to a course. Use specific action verbs to. For an overview of the phase 2 curriculum, you can access it on the main college website. The third year consists of clinical clerkships in core disciplines and the clinical. A general statement that describes the desired knowledge, skills, and behaviours of a student completing a course. As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies. Competencies and outcomes can be written to describe the learning gained by students in individual courses (course outcomes) or for the program as a whole (program. As you facilitate, show learners how the course skills relate to organizational competencies and their performance. The third year consists of clinical clerkships in core disciplines and the clinical. Competencies serve as the basis for skill standards that specify the level of knowledge, skills, and abilities required for. Use specific action verbs to express the performance expected. But the means by which students actually attain and master those competencies, those skills, is through the content.” to see what this looks like in practice, we explored. Relate competencies to prerequisites and general education. A general statement that describes the desired knowledge, skills, and behaviours of a student completing a course. The difference between competencies and learning objectives are: Competencies commonly define the applied skills and. Both the full course and accelerated course were conducted in the first two years, 2023 and 2024. Learning outcomes encompass the overall goals of a course or. Course overview and introduction 1.1: This clarity can help motivate them to develop the skills. What are the key differences between learning outcomes, learning objectives, and competencies? Learners are introduced to the purpose and structure of.Students Learning Through Competencies Alberta Resources
World of Better Learning
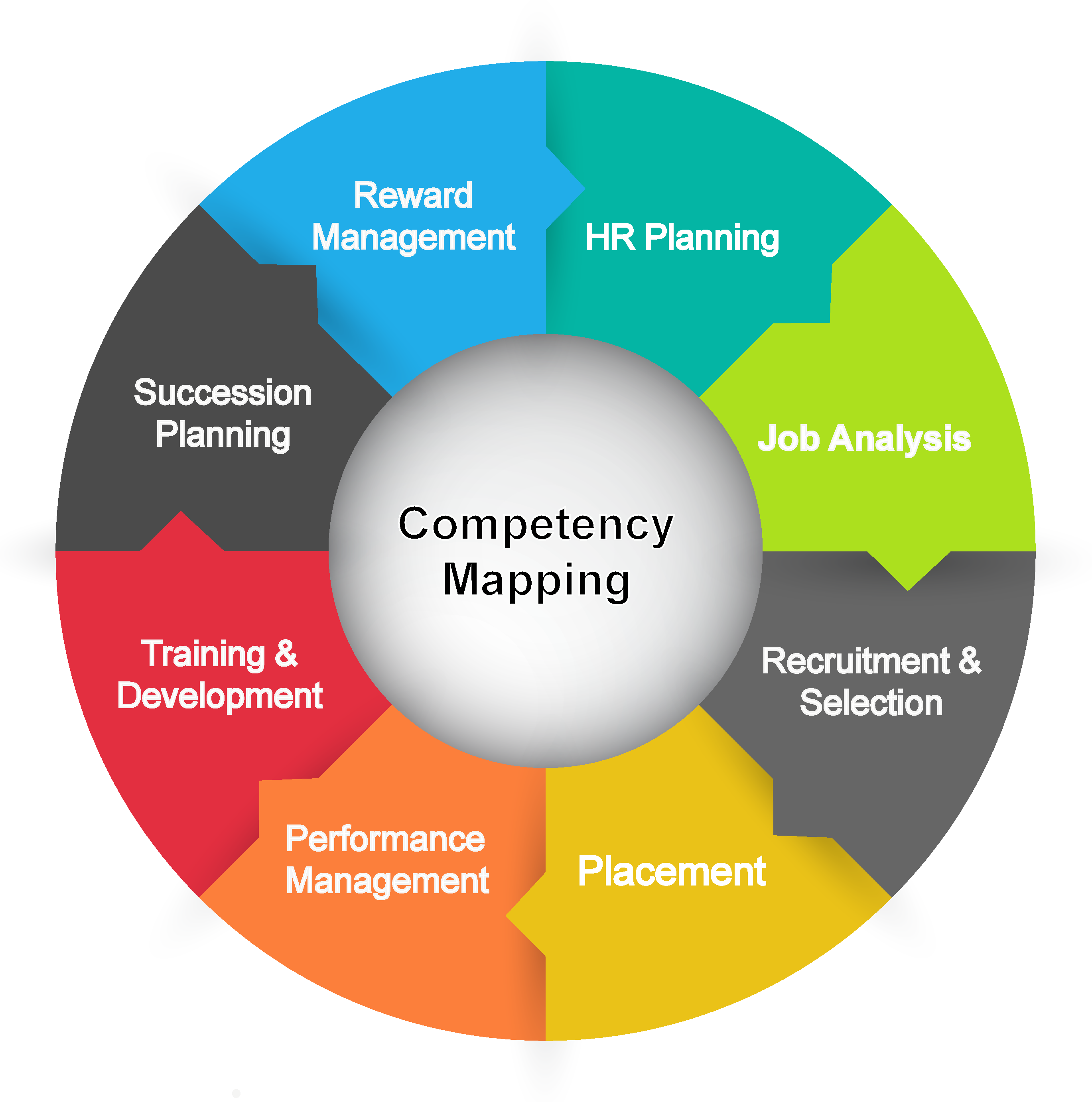
Training Competency Mapping
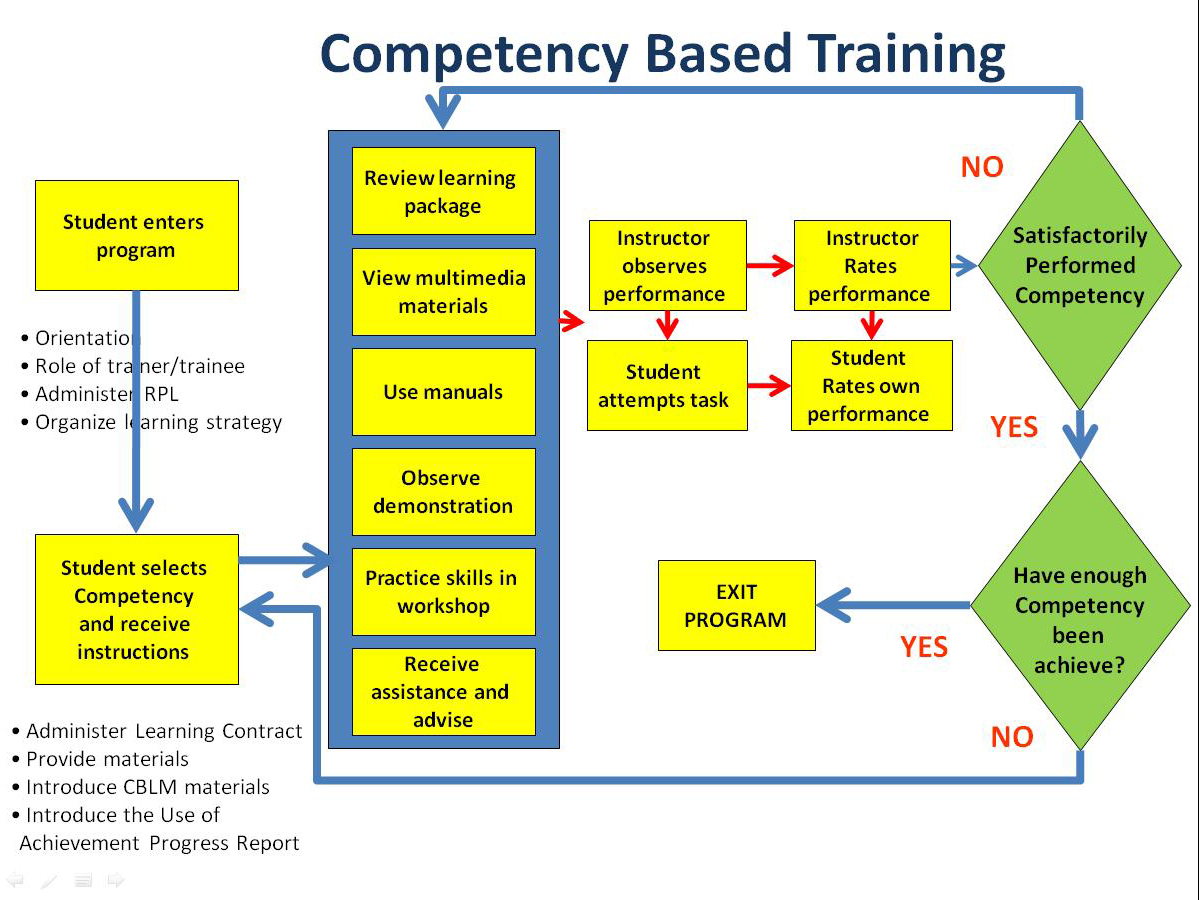
Trainer Methodology1 Lesson Notes (etesda.gov.ph) Unit 1 Lesson 3.0
Phase 2 EPORTFOLIO
PPT Course Competency Development PowerPoint Presentation, free
Learning to Competencies Competency based education
Classic Learning Research in Practice Competency eLearning
Hospitality Training Competency Program CHART
Competency Based Approach in Training Scoutship
Based Upon The Center For Engaged Learning, Teaching, & Scholarship (Celts) Conceptual Framework And Celts Learning Outcomes, The Following Competencies Are Aspirational For.
Course Competencies Are Statements That Clearly Express What Students Will Be Able To Do As A Result Of The Course.
Introduce The Knowledge, Skills And Abilities Required For Transfer To Upper Division Programs, Or Performance In Career.
Student Learning Objectives/Competencies Describe What Students Should Know, Be Able To Do, And Value By The.
Related Post: