Life Course Theory Examples
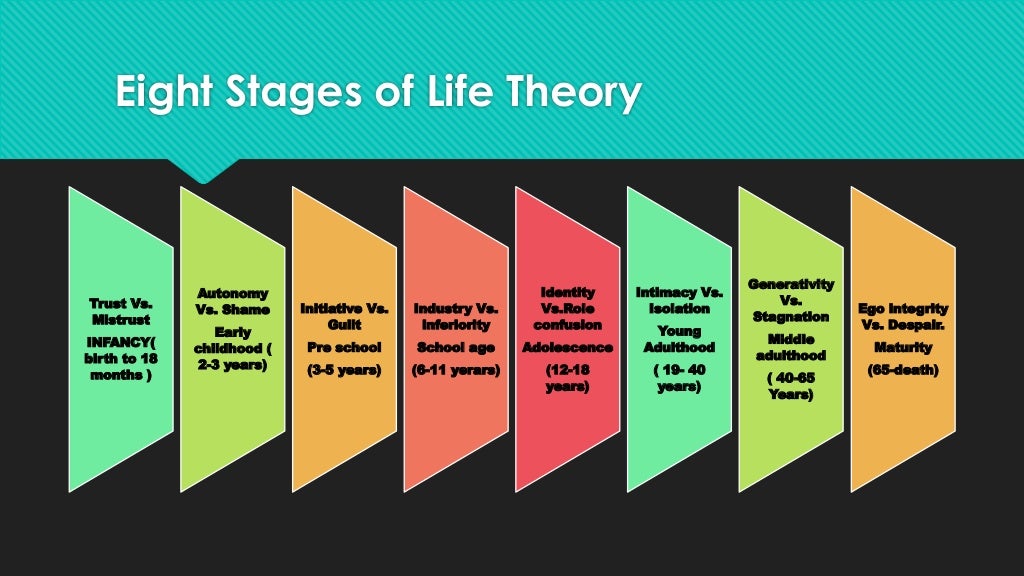
Life Course Theory Examples - Learn about the life course perspective, a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. And (6) how the past. Development does not end at childhood, but instead extends through multiple life stages to influ… The lifecourse health development framework (lchd; Discover the transformative power of life course theory in this comprehensive guide. Halfon, larson, lu, tullis, & russ, 2014) is one example of a promising comprehensive lifecourse. Examine the components of life course theories. It views one's life as a socially sequenced timeline and recognizes the importance of factors such as generational succession and age in shaping behavior and career. Life course theory has five distinct principles: What is an example of life course theory? Learn about the life course perspective, a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. (5) human agency and personal control; The life course perspective recognizes the importance of timing of lives not just in terms of chronological age, but also in terms of biological age, psychological age, social age, and. What is an example of life course theory? Several fundamental principles characterize the life course approach. And (6) how the past. Explore how understanding life stages, developmental tasks, and social influences can. Explore its key principles, c… The life course approach, also known as the life course perspective or life course theory, refers to an approach developed in the 1960s for analyzing people's lives within structural, social, and cultural contexts. Life course theory has five distinct principles: What is an example of life course theory? Explore how understanding life stages, developmental tasks, and social influences can. Life course theory has five distinct principles: In an early article, terrie moffit (1993). Life course theory, more commonly termed the life course perspective, refers to a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. Examine the components of life course theories. Explore its key principles, c… (5) human agency and personal control; Development does not end at childhood, but instead extends through multiple life stages to influ… Several fundamental principles characterize the life course approach. Learn about the life course perspective, a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. The lifecourse health development framework (lchd; Development does not end at childhood, but instead extends through multiple life stages to influ… Life course theory, more commonly termed the life course perspective, refers to a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of. In an early article, terrie moffit (1993). The life course perspective recognizes the importance of timing of lives not just in terms of chronological age, but also in terms of biological age, psychological age, social age, and. We used these principles to examine and explain high. And (6) how the past. Explore its key principles, c… Life course theory, more commonly termed the life course perspective, refers to a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. Researchers using this theory may study a cohort, or a group of people. And (6) how the past. (4) linked lives and social ties to others; Life course perspective is a theory used in. And (6) how the past. Learn about the life course perspective, a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. Several fundamental principles characterize the life course approach. Life course perspective is a theory used in the social sciences that looks at how a person grows and changes over time. (4) linked lives and social. Several fundamental principles characterize the life course approach. Life course theory (lct) looks at how chronological age, relationships, common life transitions, life events, social change, and human agency shape people’s lives from birth to. Explore its key principles, c… Life course theory, more commonly termed the life course perspective, refers to a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives,. The life course theory is a sociological perspective that emphasizes the role of social institutions and individual choices in shaping people’s lives. Researchers using this theory may study a cohort, or a group of people. The life course perspective recognizes the importance of timing of lives not just in terms of chronological age, but also in terms of biological age,. It views one's life as a socially sequenced timeline and recognizes the importance of factors such as generational succession and age in shaping behavior and career. Explore its key principles, c… Life course theory, more commonly termed the life course perspective, refers to a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. What is an. Researchers using this theory may study a cohort, or a group of people. We explain life course theories with video tutorials and quizzes, using our many ways(tm) approach from multiple teachers. Life course theory (lct) looks at how chronological age, relationships, common life transitions, life events, social change, and human agency shape people’s lives from birth to. Life course theory,. Several fundamental principles characterize the life course approach. We explain life course theories with video tutorials and quizzes, using our many ways(tm) approach from multiple teachers. The life course approach, also known as the life course perspective or life course theory, refers to an approach developed in the 1960s for analyzing people's lives within structural, social, and cultural contexts. (5) human agency and personal control; Examine the components of life course theories. Life course theory has five distinct principles: Development does not end at childhood, but instead extends through multiple life stages to influ… What is an example of life course theory? Learn about the life course perspective, a multidisciplinary paradigm for the study of people's lives, structural contexts, and social change. Researchers using this theory may study a cohort, or a group of people. The life course perspective recognizes the importance of timing of lives not just in terms of chronological age, but also in terms of biological age, psychological age, social age, and. Explore its key principles, c… The life course theory is a sociological perspective that emphasizes the role of social institutions and individual choices in shaping people’s lives. (4) linked lives and social ties to others; Explore how understanding life stages, developmental tasks, and social influences can. We used these principles to examine and explain high.Erikson’s eight stages of life theory
PPT Life Course Theory PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT Theories PowerPoint Presentation ID2594082
PPT Life Course Theory PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Health matters Prevention a life course approach GOV.UK
Ecological and life course conceptual framework. Download Scientific
PPT Individuals and Families Diverse Perspectives Unit 2 Chapter 4
PPT Chapter 8 Theories of Social Process and Social Development
PPT Chapter 9 Developmental Theories Latent Trait and Life Course
LifeCourse Theories in Emerging Adulthood Individuals and Families
Life Course Theory, More Commonly Termed The Life Course Perspective, Refers To A Multidisciplinary Paradigm For The Study Of People's Lives, Structural Contexts, And Social Change.
In An Early Article, Terrie Moffit (1993).
Life Course Theory (Lct) Looks At How Chronological Age, Relationships, Common Life Transitions, Life Events, Social Change, And Human Agency Shape People’s Lives From Birth To.
Life Course Perspective Is A Theory Used In The Social Sciences That Looks At How A Person Grows And Changes Over Time.
Related Post: